Solar Power Blog
ETFE Solar Panels, PV Technology in Simple Terms
ETFE solar panels are yet another acronym in the fast-moving field of renewable energy. With PV (photovoltaic) technology striving to lower GHGs (greenhouse gases), it can be difficult to stay up to date with the latest innovations in solar energy.
Solar Us Shop is dedicated to breaking down complex renewable energy lingo into simple terms for everyone to understand. In 2021, ETFE solar panels are one of the most commonly searched terms, so we would like to define what they are and put them into perspective with other commonly heard terms.
In this article, we hope to answer any questions you may have about ETFE solar panels and provide a better understanding of how they fit in with today’s technology.

What are ETFE Solar Panels?
An ETFE solar panel is simply a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel with ETFE film used as a protective, top layer. ETFE stands for “ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer,” which is a bit of a mouthful, so this is why most people simply refer to the film as “ETFE.” The material is made of fluorine-based plastic and is often synonymous with the most popular brand: Tefzel.
ETFE films are created by melting down ETFE particles. Generally, ETFE films are:
- Colorless
- Lightweight
- Fire and heat resistant
- Durable against harsh weather and wind
- Impermeable to UV rays
- Self-cleaning (small coefficient of friction allows for rain or snow cleanse)
- Protectively sealed against water damage
- And transparent enough to allow 95% of light to reach solar cells
Most Common ETFE Solar Panel Applications
ETFE solar panels are used in a wide variety of applications from small solar collectors to industrial PV systems. Today, ETFE films are most commonly used in semi-flexible solar panels that may undergo extreme exposure to UV, heat, or harsh weather conditions. Before installation, the material is completely malleable and able to contour to non-traditional building designs.
Can ETFE solar panels be recycled?
Yes, The ETFE film on solar panels can be recycled at the end of its lifetime, which is usually anywhere from 5 to 10 years. Oftentimes, the materials can be recycled back into another ETFE product for a truly sustainable lifecycle.
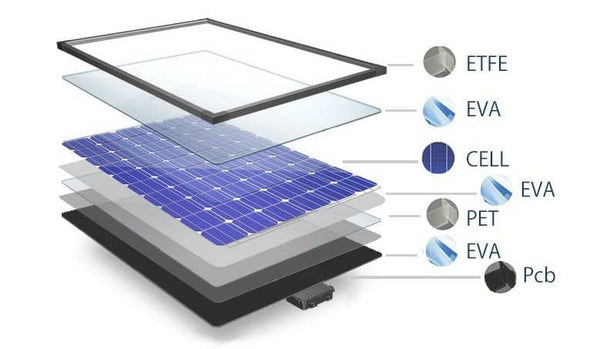
The Structure of ETFE Solar Panels
As we mentioned before, an ETFE solar panel is only defined as such if it has an ETFE top layer. Below the protective shell, ETFE solar panels are typically made with:
- An EVA film (used to further insulate and seal the solar panels)
- The solar cells (the blue or black silicon layer that actually creates the electricity)
- A second EVA film (to complete the solar cell seal)
-
And a back sheet or tedlar composite.

ETFE vs PET Solar Panels
Much like EFTE, PET is a flexible polymer that can be used as the top layer of solar panels. For this reason, the two materials draw a lot of comparisons in which ETFE solar panels quite obviously become the better choice.
PET solar panels emit a low thermal emission when in use, in that heat is released from the material. This makes them potentially hazardous to your system and its surroundings. PET solar panels are also much less efficient in capturing sunlight, can become easily damaged, and have shorter lifespans. For this reason, most modern, flexible solar panels utilize ETFE technology.
Beyond flexible polymers, many residential and commercial solar arrays are made up of rigid glass solar panels. Although glass panels certainly have their advantages, the solar panels are not flexible and also considerably heavier, which limits the broader installation possibilities.
Monocrystalline & Polycrystalline ETFE Solar Panels
With an ETFE film on top, there are two popular types of photovoltaic solar cells: monocrystalline and polycrystalline (often referred to simply as “mono” and “poly”). Monocrystalline ETFE solar panels are generally seen as the premium option, whereas polycrystalline panels are much more affordable.
Monocrystalline PV Solar Panels

For instance, take a look at the Nature Power 50-Watt Semi-Flex Monocrystalline Solar Panel. Nature Power’s sleek monocrystalline design makes this 50-Watt solar panel, ultrathin, ultralight, and extremely efficient. While $500 is nothing to shake a stick at, this durable and semi-flexible solar panel enables enormous electricity potential for RVs, boats, and off-grid homes.
Polycrystalline PV Solar Panels

Secondly, polycrystalline PV solar panels are still very useful for a number of applications, despite being less efficient. Whenever solar energy is the singular power source for an individual electronic, like in this LED Solar Flood Light, a polycrystalline panel and small battery bank is generally all that is necessary. Here, the 20W of photovoltaic panels provide plenty of energy for the high efficiency LED lights.
Thermal Solar Panels
Lastly, we would like to clear up any confusion between thermal and photovoltaic solar panels. ETFE films cannot be applied to thermal solar panels, because they are used to capture heat from the sun (and turn it into usable energy) rather than sunlight.

In North America, thermal solar panels are commonly used to heat a home’s hot water and can be installed alongside a PV array. In the image above, you can see a water tank directly above the thermal solar panel.
In an even simpler example of thermal solar heat, check out the Coleman Solar Heated Shower For Outdoor Use. This “shower-head” captures heat from the sun so that you can enjoy a warm shower wherever you are!
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, we hope that this guide has helped clear up some of the most commonly asked questions about ETFE solar panels and sun-powered technology in general. While the right choice in panels and products is always boiled down to the individual needs of the end-user, it is critical to understand what technology is best to suit any application and budget.
If you are interested in turning to solar energy for clean, renewable, off-grid electricity, we encourage you to educate yourself and explore the possibilities of all-in-one, DIY solar kits.

